Public Key Infrastructure (PKI): A Comprehensive Guide
Public Key Infrastructure (PKI): A Comprehensive Guide
Blog Article
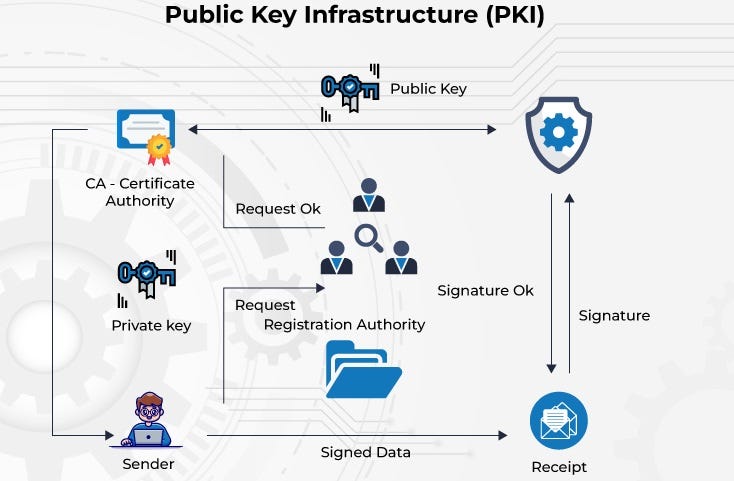
Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) is a framework of encryption and cybersecurity that secures digital communications and data exchanges. It is essential for ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity of information in a connected world. In this article, we will explore the components, workings, benefits, and applications of PKI.
Understanding Public Key Infrastructure (PKI)
PKI is a system of cryptographic technologies, policies, and procedures that enable secure electronic transactions. It provides a structured approach to digital security by using encryption and authentication mechanisms.
Key Components of PKI
PKI consists of several essential components that work together to ensure digital security:
1. Certificate Authority (CA)
- The CA is responsible for issuing, managing, and revoking digital certificates.
- It verifies the identity of users, devices, or organizations requesting a certificate.
2. Registration Authority (RA)
- Acts as an intermediary between the user and the CA.
- It validates user identity before forwarding certificate requests to the CA.
3. Digital Certificates
- Serve as electronic credentials to authenticate identities.
- Contain details such as the public key, certificate holder’s information, and CA’s signature.
4. Public and Private Keys
- PKI relies on asymmetric encryption using two keys:
- Public Key: Shared openly and used for encryption.
- Private Key: Kept confidential and used for decryption.
5. Certificate Revocation List (CRL) & Online Certificate Status Protocol (OCSP)
- CRL maintains a list of revoked certificates to prevent misuse.
- OCSP allows real-time verification of certificate validity.
How PKI Works?
PKI functions through a series of steps to secure digital interactions:
- A user or device requests a digital certificate from the CA.
- The RA verifies the requester's identity.
- The CA issues and digitally signs the certificate.
- The user or device uses the certificate for encrypted communication.
- The validity of the certificate is checked through CRL or OCSP.
Benefits of PKI
PKI offers numerous advantages in cybersecurity:
- Enhanced Security: Encrypts sensitive data to prevent unauthorized access.
- Authentication: Ensures that users and devices are legitimate.
- Data Integrity: Protects data from being altered or tampered with.
- Scalability: Can be implemented across enterprises and global networks.
- Regulatory Compliance: Helps organizations meet security and privacy standards.
Applications of PKI
PKI is widely used in various industries and applications, including:
- Secure Email Communication: Encrypts and digitally signs emails.
- SSL/TLS for Websites: Enables HTTPS for secure web browsing.
- Digital Signatures: Ensures document authenticity and legal validity.
- IoT Security: Protects connected devices and their communications.
- VPNs and Network Security: Secures remote access to networks.
Conclusion
Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) is a vital technology that ensures secure digital communication and identity authentication. By leveraging cryptographic keys, digital certificates, and secure protocols, PKI plays a crucial role in modern cybersecurity. Understanding its components and benefits helps organizations and individuals enhance their security posture effectively. Report this page